UVM - Virtual Sequencer
本文介绍UVM Virtual Sequence/Sequencer的使用。
使用场景
通常 virtual sequence 和 virtual sequencer 同时使用。
- 如果只有一个驱动端agent,显然是不需要使用virtual sequencer的。
- 如果有多的驱动端agent,但是多个激励之间并无协调关系,virtual sequencer 也并无必要。
- 如果有多的驱动端agent,而且多个激励之间存在协调关系,那么virtual sequencer就很有必要了。这个时候环境中需要包含一个甚至多个virtual sequencer了。
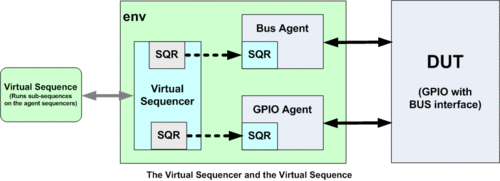
A virtual sequencer is little more than a component providing a locus and scope to configure virtual sequences and provide handles to the subsequencers that will be required by virtual sequences.
class vsequencer extends uvm_sequencer;
`uvm_component_utils(vsequencer)
tb_ahb_sequencer ahb_sqr;
tb_eth_sequencer eth_sqr;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void end_of_elaboration_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.end_of_elaboration_phase(phase);
if (!uvm_config_db#(tb_ahb_sequencer)::get(this, "", "ahb_sqr", ahb_sqr))
`uvm_fatal("VSQR/CFG/NOAHB", "No ahb_sqr specified for this instance");
if (!uvm_config_db#(tb_eth_sequencer)::get(this, "", "eth_sqr", eth_sqr))
`uvm_fatal("VSQR/CFG/NOETH", "No eth_sqr specified for this instance");
endfunction
endclass
讲解
完整的示例请参考Synopsys的Blog,Mentor Verification Academy,cnblogs以及Sunburst Design.
Notes
- Virtual sequencer has references to the sequencers we are trying to control. These references are assigned from top environment to the non-virtual sequencers.
- Virtual sequences can only associate with virtual sequencer (but not with non-virtual sequencer).
- Virtual sequence can only execute sequences or other virtual sequences but not the items。
- While configuring the variables in the sequences (which are executed using virtual sequences) we have to use path thru virtual sequence.
- Even though we have virtual sequencer to control multiple sequencers, in some tests, we may just need a single sequencer (for example USB sequencer alone). In such cases, we have to use the non-virtual sequencer’s hierarchical path directly (not the virtual sequencer’s reference path) for configuring the variables or factory overrides. Using the virtual sequencer’s reference path will not work as the hierarchy of non-virtual sequencer is incorrect.
- Whenever we are using virtual sequencer and want to control non-virtual sequencers from virtual sequencer, make sure to set the default_sequence in all the actual sequencers to null.
uvm_config_db#(uvm_object_wrapper)::set(this, “env.usb_host_agent_obj.sequencer.main_phase”, “default_sequence”, null);
p_sequencer / m_sequencer
参考eetop,以及Sunburst Design,两者的解释如下:
Every sequence has a handle to the sequencer that is running that sequence. That handle is called the m_sequencer handle. The m_sequencer handle is just a handle in every sequence that points to the sequencer that is running that sequence and it was set when the start() method was passed the handle of the sequencer. Just like any other sequence, when a virtual sequence is started on a virtual sequencer, using either the start() method or the `uvm_do macros, the virtual sequence will automatically have an m_sequencer handle that correctly points to the virtual sequencer.
The m_sequencer variable is an internal implementation variable that is poorly documented and should not be used directly by verification engineers. It is an artifact of the SystemVerilog language, which lacks C++’s concept of “friend” classes that this variable is public. Any variable or method with the “m_” prefix should similarly not be used directly.
`uvm_declare_p_sequencer宏代码如下:
`define uvm_declare_p_sequencer(SEQUENCER) \
SEQUENCER p_sequencer;\
virtual function void m_set_p_sequencer();\
super.m_set_p_sequencer(); \
if( !$cast(p_sequencer, m_sequencer)) \
`uvm_fatal("DCLPSQ", \
$sformatf("%m %s Error casting p_sequencer, please verify that this sequence/sequence item is intended to execute on this type of sequencer",
get_full_name())) \
endfunction
该部分代码实现了两件事
- 声明了一个sequencer类型的句柄p_sequencer.
- 这个宏将m_sequencer句柄转化为p_sequencer 类型的句柄。
两种句柄使用方法对比。Mentor使用了m_sequencer。
// Virtual sequence base class:
//
class virtual_sequence_base extends uvm_sequence #(uvm_sequence_item);
`uvm_object_utils(virtual_sequence_base)
// This is needed to get to the sub-sequencers in the
// m_sequencer
virtual_sequencer v_sqr;
// Local sub-sequencer handles
bus_master_sequencer bus;
gpio_sequencer gpio;
function new(string name = "virtual_sequence_base");
super.new(name);
endfunction
// Assign pointers to the sub-sequences in the base body method:
task body();
if(!$cast(v_sqr, m_sequencer)) begin
`uvm_error(get_full_name(), "Virtual sequencer pointer cast failed");
end
bus = v_sqr.bus;
gpio = v_sqr.gpio;
endtask: body
而Sunburst推荐使用的方法如下:
class vseq_base extends uvm_sequence;
`uvm_object_utils(vseq_base)
`uvm_declare_p_sequencer(vsequencer)
function new(string name="vseq_base");
super.new(name);
endfunction
tb_ahb_sequencer ahb_sqr;
tb_eth_sequencer eth_sqr;
virtual task body();
ahb_sqr = p_sequencer.ahb_sqr;
eth_sqr = p_sequencer.eth_sqr;
endtask
endclass
可以看到,Mentor的方法只是手动展开了`uvm_declare_p_sequencer的宏定义。结合上方的讨论,推荐使用p_sequencer方法.
执行 virtual sequence
Sequences are started on a sequencer using the built-in sequence start() method or by using the `uvm_do() macros.
`uvm_do方法较为简单,但在仿真上较为低效(sub-sequences are always allocated and randomized before being executed)。
task body();
// ...
//executingnon-virtual sequence on the corresponding
//non-virtual sequencer using `uvm_do_on
`uvm_do_on(a_reset_seq, p_sequencer.axi_seqr)
a_reset_seq.get_response();
`uvm_do_on(u_reset_seq, p_sequencer.usb_seqr)
u_reset_seq.get_response();
endtask: body
注:Use `uvm_do_on/`uvm_do_on_with to execute non-virtual sequences and `uvm_do/`uvm_do_with to execute other virtual sequences.
推荐显式调用randomize()和start()方法。
virtual task body();
ahb_seq1 ahb_seq = ahb_seq1::type_id::create("ahb_seq");
eth_seq1 eth_seq = eth_seq1::type_id::create("eth_seq");
//---------------------------------------------------
super.body();
`uvm_info("v_seq2", "Executing sequence", UVM_HIGH)
if(!ahb_seq.randomize()) `uvm_error("RAND","FAILED");
ahb_seq.start(ahb_sqr);
if(!eth_seq.randomize()) `uvm_error("RAND","FAILED");
eth_seq.start(eth_sqr);
if(!eth_seq.randomize()) `uvm_error("RAND","FAILED");
eth_seq.start(eth_sqr);
if(!ahb_seq.randomize()) `uvm_error("RAND","FAILED");
ahb_seq.start(ahb_sqr);
`uvm_info("v_seq2", "Sequence complete", UVM_HIGH)
endtask
sequencer 句柄传递
在Env中,向virtual sequencer中传递sequencer句柄的方式有两种,一种直接通过层次化引用传递;另一种通过config_db机制。
// class my_env extends uvm_env
function void connect_phase();
// 直接通过指针传递实例化的driver sequencer
v_sequencer.cpu_seqr = cpu0.master[0].sequencer;
// 通过config_db机制传递实例化的driver sequencer
uvm_config_db#(uvm_sequencer)::set(this,”v_sequencer”,
”eth_seqr”,eth0.tx_rx_agent.sequencer);
endfunction : connect
启动 virtual seqneces
n general, virtual sequences are started from a test using the sequence start() method. It is a good idea to create a test_base class with common declarations and methods that will be used by every other test in the verification suite. Once a test_base class is coded, each of the tests can extend the test_base to create the individual tests.
class test_base extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test_base)
env e;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
e = env::type_id::create("e", this);
endfunction
function void start_of_simulation_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.start_of_simulation_phase(phase);
if (uvm_report_enabled(UVM_HIGH)) begin
this.print();
factory.print();
end
endfunction
endclass
////////////////////////////
////////////////////////////
`timescale 1ns/1ns
class test1 extends test_base;
`uvm_component_utils(test1)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
v_seq1 vseq = v_seq1::type_id::create("vseq");
uvm_test_done.raise_objection(this);
`uvm_info("test1 run", "Starting test", UVM_MEDIUM)
vseq.start(e.v_sqr);
`uvm_info("test1 run", "Ending test", UVM_MEDIUM)
uvm_test_done.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
Sequence Library
As the name suggests, it keeps a track of the sequences that are registered with it, and calls them a number of times in a random fashion.
class my_seq_lib_v2 extends uvm_sequence_library #(my_data);
`uvm_object_utils (my_seq_lib_v2)
`uvm_sequence_library_utils (my_seq_lib_v2)
function new (string name="my_seq_lib_v2");
super.new (name);
init_sequence_library();
endfunction
endclass
class feature_test extends base_test;
`uvm_component_utils (feature_test)
my_seq_lib m_seq_lib0;
seq1 m_seq1;
seq2 m_seq2;
seq3 m_seq3;
function new (string name, uvm_component parent = null);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase (uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase (phase);
m_seq_lib0 = my_seq_lib::type_id::create ("m_seq_lib0");
endfunction
virtual task configure_phase (uvm_phase phase);
super.configure_phase (phase);
`uvm_info ("CFG_PHASE", "Add sequences to library", UVM_MEDIUM)
m_seq_lib0.selection_mode = UVM_SEQ_LIB_RANDC;
m_seq_lib0.min_random_count = 5;
m_seq_lib0.max_random_count = 10;
m_seq_lib0.add_typewide_sequence (m_seq1.get_type());
m_seq_lib0.add_typewide_sequence (m_seq2.get_type());
m_seq_lib0.add_typewide_sequence (m_seq3.get_type());
m_seq_lib0.init_sequence_library();
endtask
function void start_of_simulation_phase (uvm_phase phase);
super.start_of_simulation_phase (phase);
uvm_config_db#(uvm_sequence_base)::set(this,"m_top_env.m_seqr0.main_phase",
"default_sequence", m_seq_lib0);
endfunction
endclass
总结
本文综合了几篇教程的内容,探讨了virtual sequence/sequencer实现上的细节差异。
- Virtual sequence/sequencer 用于带多个激励agents的环境。
- 推荐使用p_sequencer的方法。
- 在Env中,向virtual sequencer中传递sequencer句柄.
- 在virtual sequence中推荐使用start()方法启动。
- 在test中,使用start()方法启动virtual sequencer.
- sequence library 可以用来在多个Sequence之间randomize。但sequence的序列无法手动控制。
Leave a comment