UVM - Stand-alone Virtual Sequence
本文介绍 Stand-alone Virutal Sequence 的使用
stand-alone virtual sequence
在Mentor Verification Academy中,将virtual sequencer的方法称为 legacy alternative. 本文探讨其中区别。
Discussions
通过搜索找到来自accellera 以及 Verification Academy的讨论帖。
I’ll give you reason why I avoid virtual sequencer.
- You need to create virtual sequence for the virtual sequencer + sub sequences in virtual sequence have fixed sequencer on which they runs.
- This means, one needs to make way around if she’s to have multiple instance of a agent component, and previously created sub-sequences cannot be used as sequencer for them is fixed.
- Even if one wants to start a sequence on a sequencer, virtual sequence containing the sequence is needed thus increasing one more layer of sequence(virtual sequence).
Advantage of using only virtual sequence(and not virtual sequencer) is that one can contain group of sub-sequences in a higher layer called virtual sequence and start this virtual sequence on a ‘null’ sequencer.
- Optionally one can have all sequences(sub-sequences) called in test so as to avoid even virtual sequence.
- Benefit here is to group set sub-sequences in a virtual sequences if they are used frequently, so to avoid calling each sequence separately from test.
There is no need to include a virtual sequencer in either the test or the environment. All the virtual sequencer does is add more inter-component connections and complexity to the environment, with no benefit of portability nor flexibility.
尽管有人坚持认为virtual sequencer的方法没有什么不妥,但从实际使用角度来看,virtual sequencer确实只当了容器,且每个virtual sequence都有自己实际的sequencer,不使用virtual sequencer在代码编写上也方便许多,因此我赞成使用stand-alone virtual sequence的方法。
另外,实际上sequencer的作用在整个UVM中也不明显,是否…
Example
示例来自Verification Academy。由于没有virtual sequencer,对应的block level结构如下:
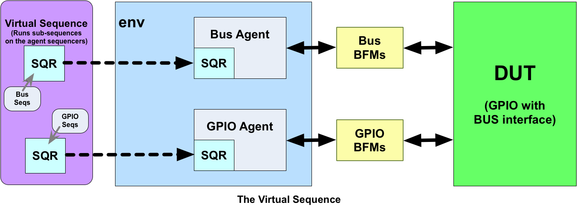
以下图所示的结构作为示例。
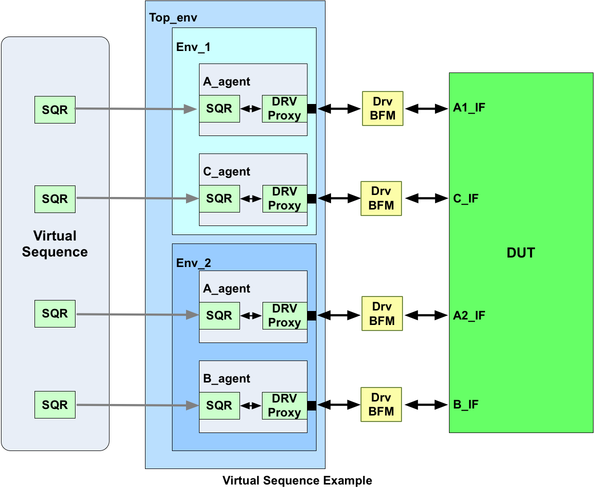
Virtual sequence包括了各个目标sequence。
class top_vseq_base extends uvm_sequence #(uvm_sequence_item);
`uvm_object_utils(top_vseq_base)
uvm_sequencer #(a_seq_item) A1;
uvm_sequencer #(a_seq_item) A2;
uvm_sequencer #(b_seq_item) B;
uvm_sequencer #(c_seq_item) C;
function new(string name = "top_vseq_base");
super.new(name);
endfunction
endclass: top_vseq_base
在test base class中,创建init_vseq函数。
class test_top_base extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test_top_base)
env_top m_env;
function new(string name = "test_top_base", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
m_env = env_top::type_id::create("m_env", this);
endfunction: build_phase
// Method to initialize the virtual sequence handles
function void init_vseq(top_vseq_base vseq);
vseq.A1 = m_env.m_env_1.m_agent_a.m_sequencer;
vseq.C = m_env.m_env_1.m_agent_c.m_sequencer;
vseq.A2 = m_env.m_env_2.m_agent_a.m_sequencer;
vseq.B = m_env.m_env_2.m_agent_b.m_sequencer;
endfunction: init_vseq
endclass: test_top_base
在派生的test class中,启动virtual sequence之前,调用init_vseq()函数。
class init_vseq_from_test extends test_top_base;
`uvm_component_utils(init_vseq_from_test)
function new(string name = "init_vseq_from_test", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
vseq_A1_B_C vseq = vseq_A1_B_C::type_id::create("vseq");
phase.raise_objection(this);
init_vseq(vseq); // Using method from test base class to assign sequence handles
vseq.start(null); // null because no target sequencer
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask: run_phase
endclass: init_vseq_from_test
其中vseq_A1_B_C是top_vseq_base的派生类
class vseq_A1_B_C extends top_vseq_base;
`uvm_object_utils(vseq_A1_B_C)
function new(string name = "vseq_A1_B_C");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task body();
a_seq a = a_seq::type_id::create("a");
b_seq b = b_seq::type_id::create("b");
c_seq c = c_seq::type_id::create("c");
a.start(A1);
fork
b.start(B);
c.start(C);
join
endtask: body
endclass: vseq_A1_B_C
其他方法
Verification Academy还提出了其他一些方法,主要的想法是将 init_vseq() 函数从test_top_base类中独立出来。
- 将initiliazation过程放在一个 test package中。这样可以同时有很多不同的initilization方法, 而不需要重新钉哥多个test base class。
- 将initiliazation过程放在一个 mapping package中,并且使用env作为参数。
package my_virtual_sequence_mapping_pkg;
//
// This package is specific to the test env and to the virtual sequence
//
import my_sequence_pkg::*;
import my_env_pkg:*;
function void init_my_virtual_sequence_from_my_env( my_virtual_sequence vseq , my_env env );
vseq.fabric_ports[0] = env.env1.a_agent.sequencer;
vseq.fabric_ports[1] = env.env2.a_agent.sequencer;
vseq.data_port = env.env1.b_agent.sequencer;
vseq.control_port = env.env2.c_agent.sequencer;
end
// Other virtual sequence initialization methods could also be defined
endpackage
- 在env中,使用uvm_config_dg传递函数句柄。该方法与virtual sequencer中提到的方法类似。
// Inside the env containing the target sequencers:
//
function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
//
uvm_config_db #(a_sequencer)::set(null, "Sequencers", "a_sqr", a_agent.m_sequencer);
uvm_config_db #(b_sequencer)::set(null, "Sequencers", "b_sqr", b_agent.m_sequencer);
//
endfunction
// Inside the virtual sequence base class:
//
a_sequencer A;
b_sequencer B;
// Get the sequencer handles back from the config_db
//
task body();
if(!uvm_config_db #(a_sequencer)::get(null, "Sequencers", "a_sqr", A)) begin
`uvm_error("body", "a_sqr of type a_sequencer not found in the uvm_config_db")
end
if(!uvm_config_db #(b_sequencer)::get(null, "Sequencers", "b_sqr", B)) begin
`uvm_error("body", "b_sqr of type b_sequencer not found in the uvm_config_db")
end
// ....
endtask
- 使用 find_all()方法。
//
// A virtual sequence which runs stand-alone, but finds its own sequencers
class virtual_sequence_base extends uvm_sequence #(uvm_sequence_item);
`uvm_object_utils(virtual_sequence)
// Sub-Sequencer handles
bus_sequencer_a A;
gpio_sequencer_b B;
// This task would be called as super.body by inheriting classes
task body;
get_sequencers();
endtask: body
//
function void get_sequencers;
uvm_component tmp[$];
//find the A sequencer in the testbench
tmp.delete(); //Make sure the queue is empty
uvm_top.find_all("*m_bus_agent_h.m_sequencer_h", tmp);
if (tmp.size() == 0)
`uvm_fatal(report_id, "Failed to find mem sequencer")
else if (tmp.size() > 1)
`uvm_fatal(report_id, "Matched too many components when looking for mem sequencer")
else
$cast(A, tmp[0]);
//find the B sequencer in the testbench
tmp.delete(); //Make sure the queue is empty
uvm_top.find_all("*m_gpio_agent_h.m_sequencer_h", tmp);
if (tmp.size() == 0)
`uvm_fatal(report_id, "Failed to find mem sequencer")
else if (tmp.size() > 1)
`uvm_fatal(report_id, "Matched too many components when looking for mem sequencer")
else
$cast(B, tmp[0]);
endfunction: get_sequences
endclass: virtual_sequence_base
注意,后两种方法都只适用于小型的结构,大结构中容易出错,不建议使用。
总结
相比virtual sequencer的方法,stand-alone virtual sequence的确显得简洁高效,且不容易出错。推荐使用stand-alone virtual sequence, 不使用 virtual sequencer。
Leave a comment